2024 was studied with scientific discoveries for defining records. From tracing the origin of shiny to dark animals to the development of the fastest microscope in the world, these superlative deeds captured our imagination.
Ancient Airburst
About 2.5 million years ago, an asteroid burned in the Earth’s atmosphere before it could hit the Earth and leave a crater, making the event the oldest the middle of the middle. This conclusion is based on a chemical analysis of nearly 120 microscopic rocks buried deep under the Antarctic ice. Ancient pebbles are rich in Olivine and Spinel minerals, suggesting that specimens are asteroid residues, scientists say.
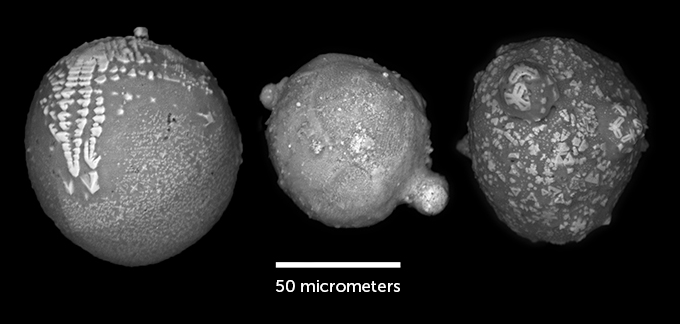
Dawn of photosynthesis
Microfosiles in Australia have the oldest photosynthesis evidence. Fossilized bacteria dating back about 1.75 billion years ago preserve structures that resemble tilacoid membranes, which help modern cyanobacteria turn sunlight into oxygen. Scientists had previously suspected that cyanobacters were photosynthesizing at the time, but the new finding is the first direct test.
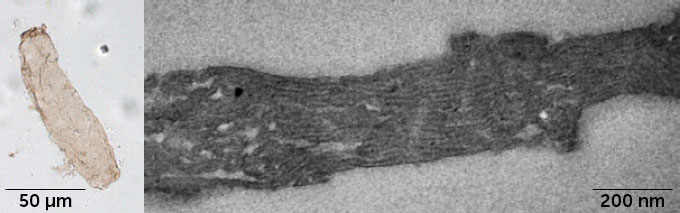
Backflip fastest
Dicyrtomina minutes Springtails can start itself up to 60 millimeters in the air and rotate at a rate of up to 368 times per second, making arthropods faster known rear (Sn: 10/5/24, p. 4). An attachment in Underbelly helps to make miniature gymnasts rise while another helps them to sit down.

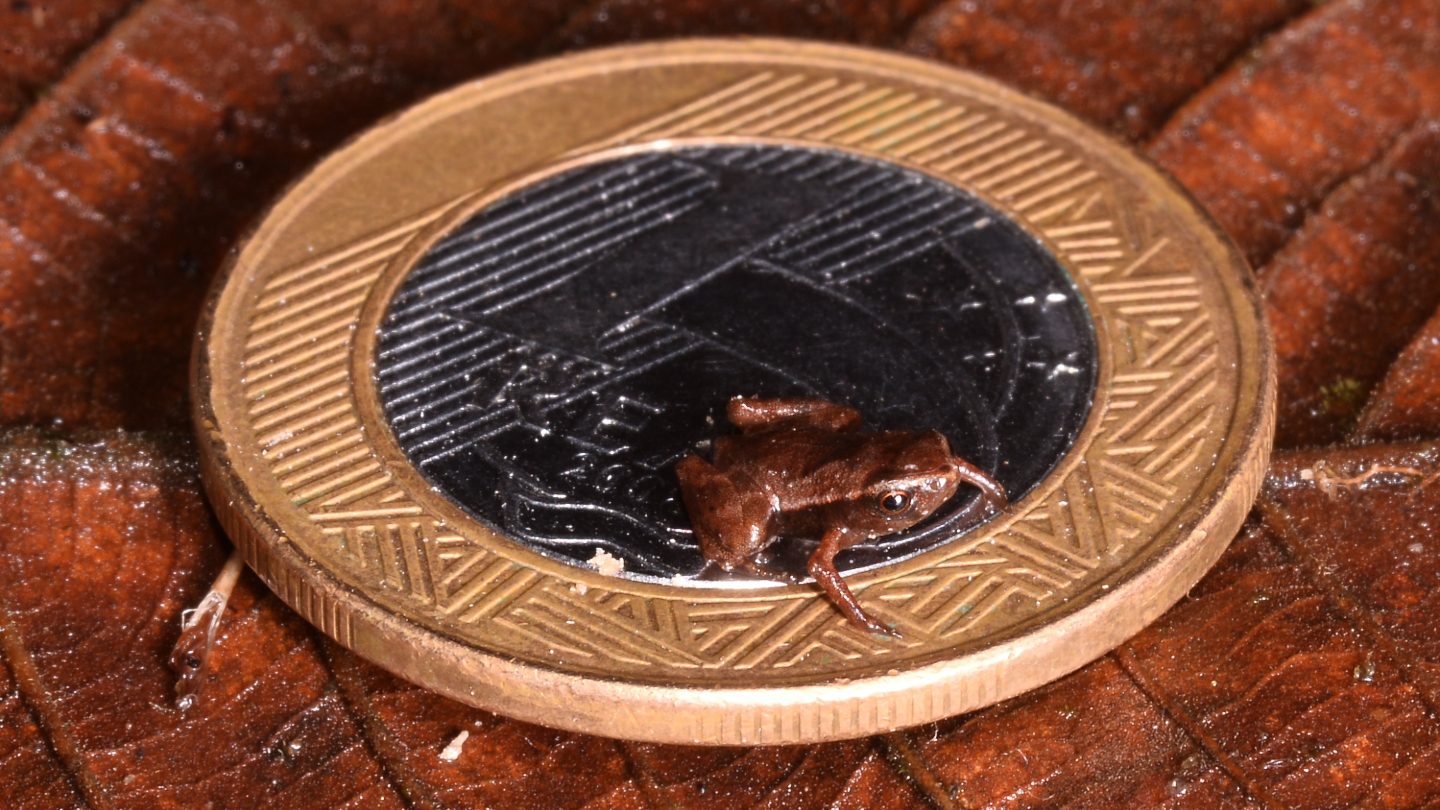
Frog Wee-on
With only 6.5 millimeters long, a Brazilian flea toad (Brachycephalus Pullex) is crowned the smallest known frog in the world (Sn: 3/23/24, p. 4). Finely enough to sit on a rose finger nail, the amphibians beat the previous sample by about a millimeter.

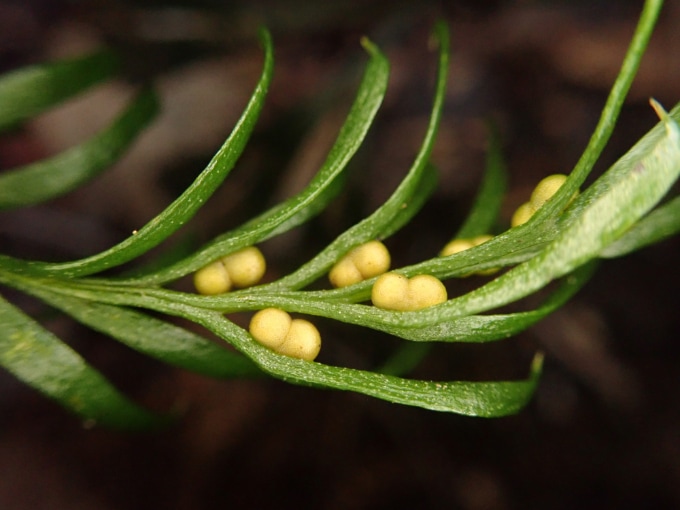
Great genome, small bundle
The largest known genetic guideline manual belongs to a small fern (Sn: 6/29/24, p. 4). Tmesipteris obranceolates It is 15 centimeters tall, but possesses a genome that is 50 times larger than humans. If discovered, Fern’s DNA spool would extend 100 meters long, scientists say.

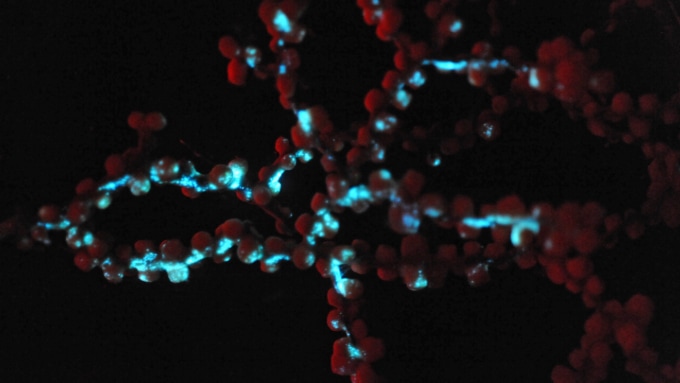
Older bioluminescence
Bioluminescence has a new birthday. The ancestors of a group of deep sea corals shone in the dark 540 million years ago, scientists say. Scientists had thought that animal bioluminescence began about 267 million years ago on a small seafood, seeds in the form of seeds.
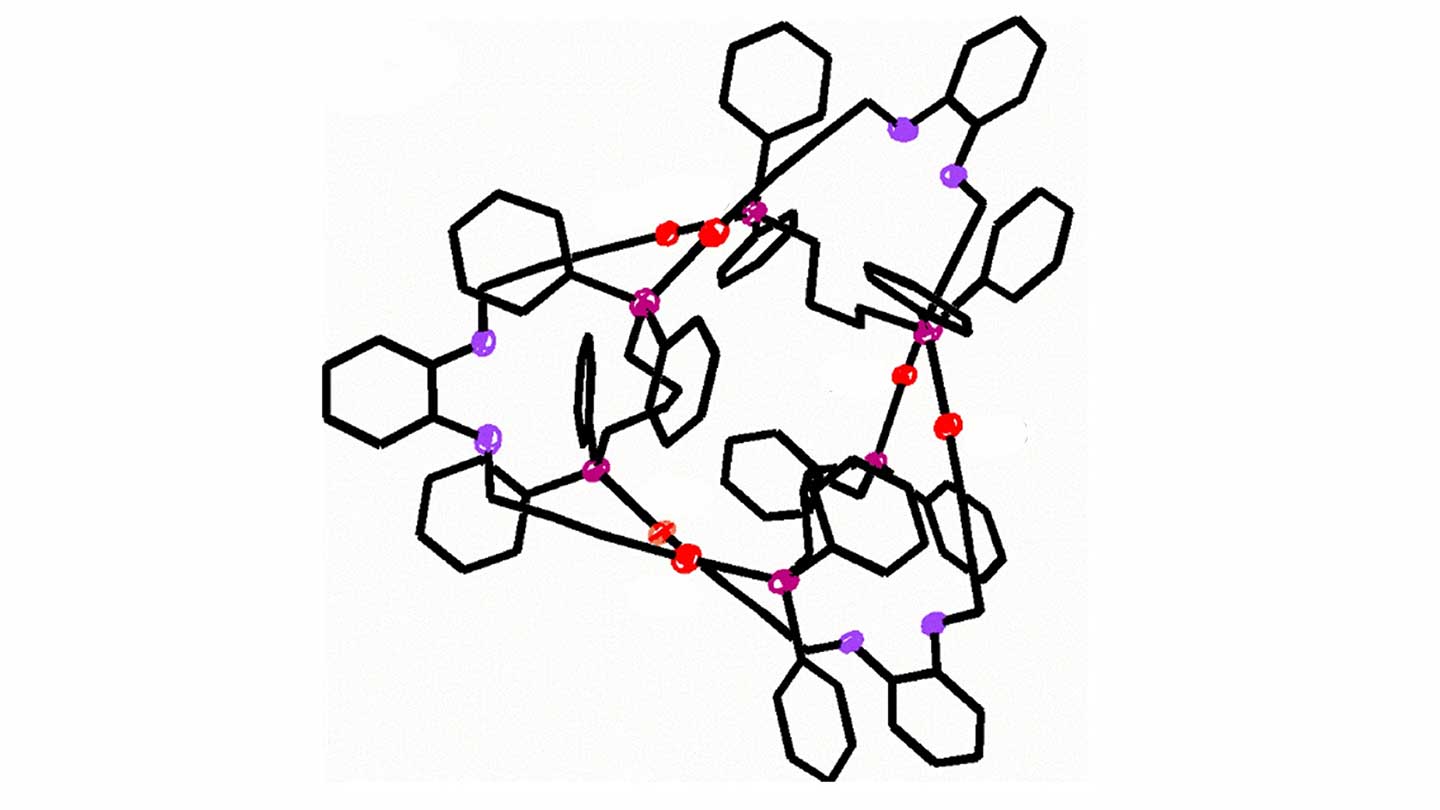
knot
The joints come in all shapes and sizes. The small figure-the eight knots keep people as they scaling the rocks. Bigger Bowlines provide ships ashore. This year, scientists designed the smallest and narrower knot yet (Sn: 2/24/24, p. 4). This trefail knot is made of a range of 54 atoms of gold, phosphorus, oxygen and carbon that is predetermined over itself three times.
#scientific #deeds #set #records
Image Source : www.sciencenews.org